Ghori’s Conquest: The Making of an Empire
Ghori’s Conquest over Prithviraj Chauhan has been a game changing moment for the history o f India and Hindu kingdoms in Hindu lands of the region. Muhammad Ghori, also known as Mu’izz ad-Din Muhammad, was a ruler who changed South Asia’s history. He led many wars in India and started Muslim rule in this area. His actions have left a deep mark on history.
Thesis Statement
This essay explores Muhammad Ghori’s extensive military campaigns across the Indian subcontinent and assesses their lasting impact. More than just a series of conquests, Ghori’s actions initiated a profound transformation in the region’s political, social, and cultural landscapes. His legacy is a complex tapestry of influence that laid the groundwork for the subsequent centuries of Islamic rule in India. This thesis will delve into how Ghori’s rule not only changed the course of Indian history but also contributed to the rich, multifaceted cultural synthesis that characterizes the subcontinent today.
Ghori’s Early Life, Conquest and Rise to Power
Birth and Early Years
Muhammad Ghori was born in the Ghor region of today’s Afghanistan. Little is known about his early life. But, his family ruled Ghor, which set his path to power.
Rise to Power
Ghori became a leader after his brother. He fought his neighbors first. Then, he looked to India for more land. He won and lost some early battles but kept trying. His will to keep fighting showed his strength as a ruler.
Ghori’s Conquests in Northern India
First Invasions
Muhammad Ghori first invaded India in the late 12th century. He faced tough resistance and suffered defeats. These setbacks did not stop him. He was determined to conquer more lands.
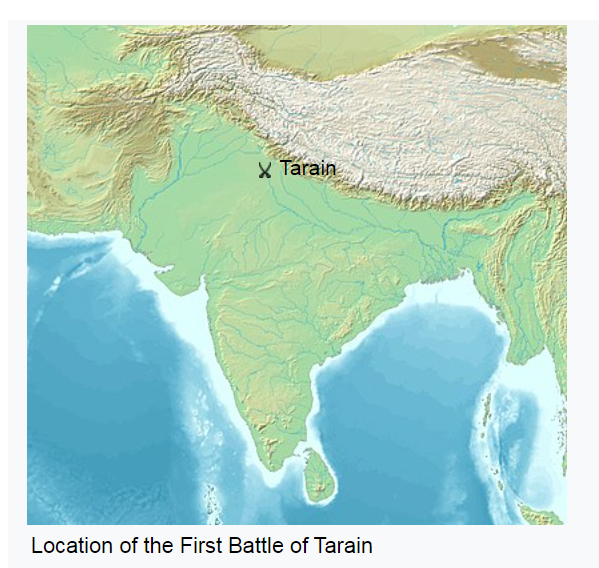
Battles of Tarain
Ghori fought two major battles at Tarain. In the first battle, he was defeated by Prithviraj Chauhan. But Ghori came back stronger in the second battle. He used better tactics and won. This victory was a turning point.
Ghori’s Conquest and Expansion of Territory
After Tarain, Ghori’s army fought many battles. They made deals with local leaders. These steps helped Ghori grow his area of control in Northern India.
Comparative Analysis of Muhammad Ghori’s Rule
Military Ambition and Execution
Contrast with Southern Dynasties
While the Chalukyas and Cholas focused on temple networks and trade, Ghori was engaged in military expansion, setting him apart with his focus on creating a centralized Islamic empire.
Ghori vs. Prithviraj Chauhan
A direct comparison with Prithviraj Chauhan showcasaes Ghori’s offensive military strategy, resilience, and expansive ambition, contrasted with Chauhan’s defensive and alliance-focused governance.
Governance and Administration
Innovative Use of Local Leaders
Unlike the Rajput’s feudal system, Ghori utilized converted local leaders for governance, highlighting his strategic approach to administration and control over diverse territories.
Cultural Integration and Promotion
Introduction of Persian Culture
Ghori’s introduction of Persian in administration and promotion of Islamic culture is a stark contrast to the regional cultural promotion by dynasties like the Yadavas and Hoysalas.
Ghori’s Unique Leadership Approach
This section emphasizes how Ghori’s rule was characterized by aggressive expansionism and resilience, setting a precedent for subsequent Islamic rulers in the subcontinent. His innovative governance techniques and cultural integration strategies were markedly different from his contemporaries, underscoring his role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of the region.
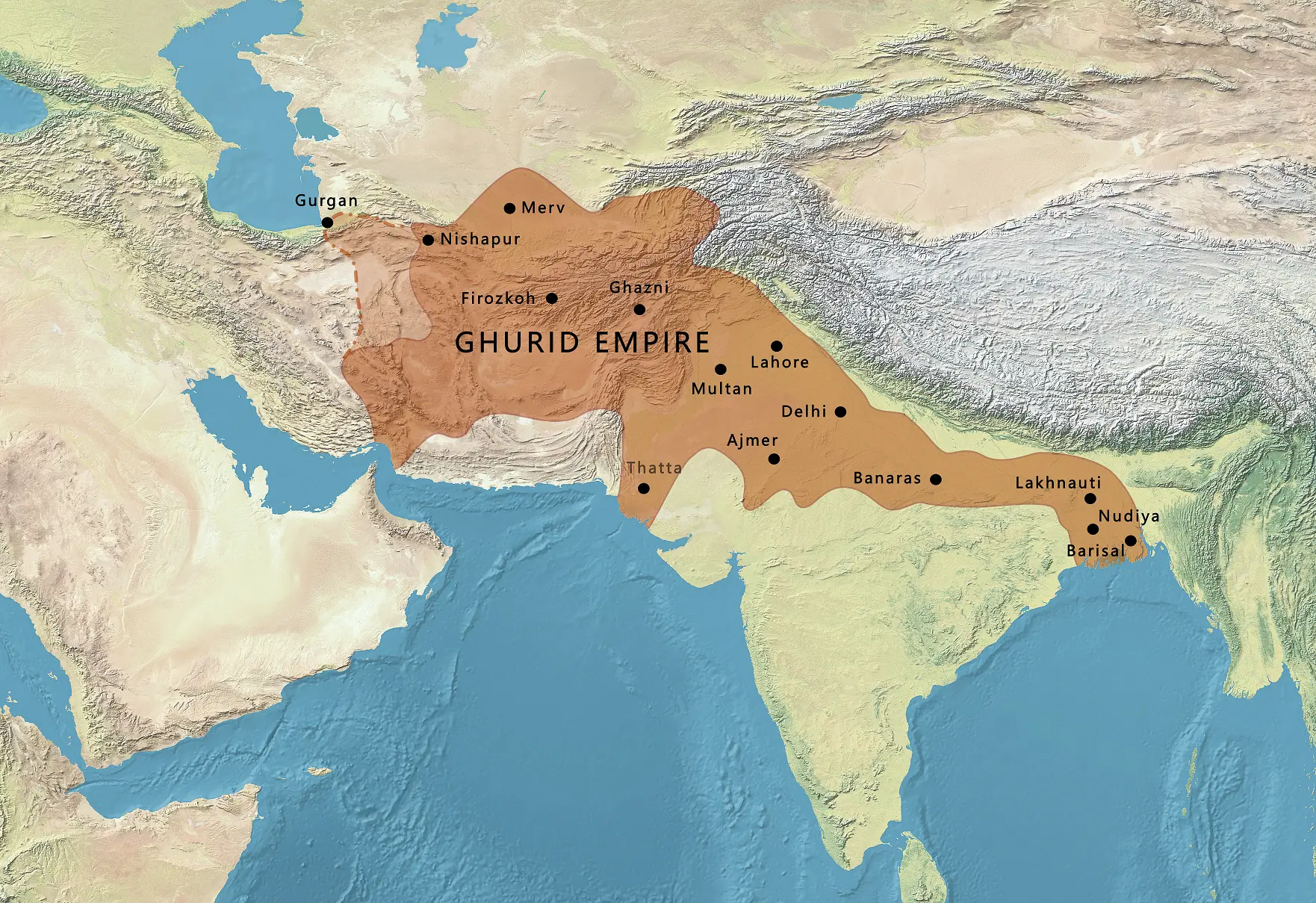
Purpose and Impact of His Wars
Extent of the Ghuri Empire showcasing key cities and regions under its dominion.(https://hinduinfopedia.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Ghurid_Empire_according_to_Schwartzberg_Atlas_p.147_wikipedia.webp)
Maps of Conquests and Territories
To better visualize the extent of Ghori’s empire, a series of maps can be included. These would illustrate the regions before his conquests, the areas affected by key battles, and the final territorial reach of his rule. This visual progression would help readers understand the scale of Ghori’s expansion.
Battle Illustrations
Illustrations of the First and Second Battles of Tarain could give insights into the tactics and formations used by Ghori’s forces. These artistic renditions would bring to life the strategic maneuvers that were pivotal in his military success.
Architectural Developments
Photographs or artist’s renderings of the mosques and madrasas established during Ghori’s rule can showcase the architectural influence of Islamic culture. Comparing these with existing structures from other cultures in the region would highlight the cultural synthesis under Ghori’s administration.
Cultural Transition Diagrams
Flowcharts or diagrams could depict the integration of Persian language and Islamic practices with the diverse cultures of the Indian subcontinent. This would visually communicate the complex process of cultural integration and its lasting impact.
Summary
We looked at Muhammad Ghori’s life. He fought many wars and took over North India. He tried to rule well and let people keep their ways. But he also wanted more power. His death is a mystery. His rule changed India for a long time.
Significance
Muhammad Ghori left a big mark on South Asia’s history. He started Muslim kingdoms in India. This change is a big part of the history books. His wars and rule are still talked about today.
Feature Image: The image is a topographic map of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. It shows the geographical features such as the mountain ranges in the north and the plains. There is a marker labeled “Tarain” indicating the location of the First Battle of Tarain on the map. (https://hinduinfopedia.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/battles-at-Tarain.png) [Credit https://www.wikipedia.org]